#
Concepts
#
System Prompt
The System Prompt is a persistent set of instructions that defines the role, purpose, tone, behavior, and constraints of a Digital Expert.
It serves as the foundational guidance that the model follows for the entire interaction, influencing how it interprets user requests and delivers responses.
In Purple Fabric, the System Prompt is configured through the Perspective field and typically includes:
Role: The specific identity of the Digital Expert or Team of Agents.
Persona: The communication style (e.g., formal, concise, customer‑friendly).
Goals & Responsibilities: The tasks the Digital Expert is expected to perform.
Guidelines: Formatting, tone, and content rules.
Outcome Presentation: Preferred format for presenting results (e.g., bullet points, tables, summaries).
This prompt is not visible to the end‑user but affects every response.
Example: “You are a financial compliance Digital Expert for a retail bank. Explain regulatory requirements in clear, concise language, avoid unnecessary jargon, and where possible, provide relevant banking examples. Present findings in bullet points with key takeaways.”
#
User Prompt
The User Prompt is the immediate request, question, or instruction given by the user during an interaction.
It changes with each query and is interpreted in the context of the System Prompt.
While the System Prompt defines how the Digital Expert should respond, the User Prompt specifies what the Digital Expert should respond to at that moment.
Example: “Summarize the key changes in Basel III banking regulations for 2025 and explain how they affect Tier 1 capital requirements.”
Tokens
The fundamental unit of text processing for Large Language Models (LLMs) within Purple Fabric. A token can be a word, part of a word, or punctuation, used to measure the length of prompts and responses. Tokens are the basis for managing LLM performance and cost. Tracking usage ensures agents operate efficiently within predefined limits, preventing unexpected costs.
Pre‑requisite: Tokens are an inherent part of LLM processing. They are automatically consumed during every agent interaction.
Example: A simple query might use 5 tokens, while a detailed agent response could use 100-200.
#
Models
Models are the foundational AI components that enable your agents to comprehend, reason, and generate responses. You select and configure these models for specific task requirements.
Large Language Model (LLM)
A LLM is the “brain” of your AI agents — a powerful system that understands and generates human language. It enables agents to interpret context, infer meaning, and respond naturally to user inputs.- **Example Use: **In Purple Fabric, an LLM powers a customer support agent to read a user’s query, understand the intent, and craft a relevant, conversational reply in real time.
**Embedding Models ** Embedding models turn text into numeric patterns that capture meaning.
To better understand refer the Embedding page**Re-ranker ** A reranker is a component in an advanced search system that refines the initial list of results. To better understand, refer to the Re-ranker page.
#
Prompt Engineering
Prompt Engineering is the strategic process of crafting precise inputs for your Digital Experts.
Purpose: Guides the agent towards desired outputs and behaviors.
Benefit: Optimizes agent understanding and response quality, preventing undesirable outcomes.
Perspective
Definition: Foundational directives defining the core identity, persona, and operational guidelines.
Configuration: Define the role, tone, and ethical boundaries.
Impact: Shapes prompt interpretation and response style for consistency.
Experience
Definition: Curated input-output pairs demonstrating desired business outcome.
Purpose: Fine-tunes the understanding of complex queries.
Benefit: Improves consistent and accurate performance in real-world interactions.
#
AI Agent
AI Agents are autonomous AI programs performing tasks based on their configurations.
Configuration: You configure them with models, knowledge sources, and tools.
Capability: Understand prompts, process information, and complete specific tasks.
#
Tools
Tools in Purple Fabric include external applications, connectors, and utilities that AI agents can use to extend their capabilities.
For detailed definition, refer to the Tool page.
#
Digital Expert
A Digital Expert is an intelligent AI‑driven solution designed to perform specific business functions and handle compound tasks that require multi‑step reasoning or actions.
Purpose: Provides specialized knowledge or automates complex operational processes.
Role: Acts as a dedicated, virtual partner, augmenting human capabilities.
Focus: Tailored to specific domains for deep expertise.
#
Team of Agents
A Team of Agents is a collaborative group of individual AI agents.
Purpose: Tackles complex, multi-faceted business objectives.
Collaboration: Each agent contributes specialized capabilities.
Mechanism: Works through defined communication protocols and handoff mechanisms to achieve shared goals.
#
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
RAG enhances an LLM’s knowledge with reliable, verified, and domain‑specific data from trusted sources.
Mechanism: "Grounds" agent responses in your verified enterprise knowledge base.
Benefit: Significantly reduces "hallucinations" and improves factual accuracy.
Outcome: Provides relevant, context‑rich information to improve the accuracy and trustworthiness of outputs.
#
ReAct Framework
The ReAct Framework combines Reasoning with Acting capabilities in a team of agents working together.
Function: Enables the team to plan and adjust sequences of decisions and actions dynamically.
Capability: Collaborates intelligently, uses tools, and retrieves targeted information when needed.
Result: Forms a decision‑driven, flexible, and adaptive problem‑solving loop.
Example: In a loan approval workflow, one agent verifies customer documents, another checks credit history, and a third applies lending rules. The team decides the next steps based on each result, ensuring accurate and compliant approvals.
#
Agent Configurations
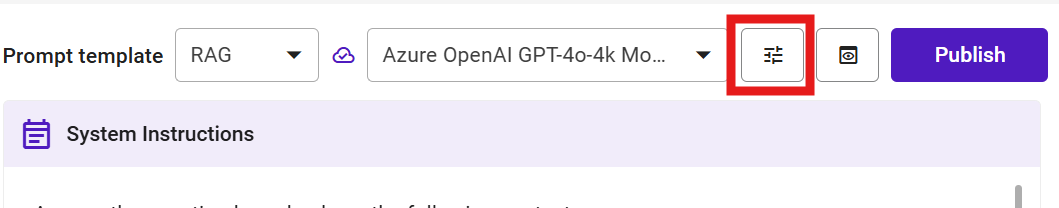
#
Models
You configure the models that provide computational intelligence for your Digital Expert.
- Selecting LLM Models
Function: Select foundational LLM.
Impact: Determines the agent's general knowledge, reasoning, and language generation.
#
Lookback Limit
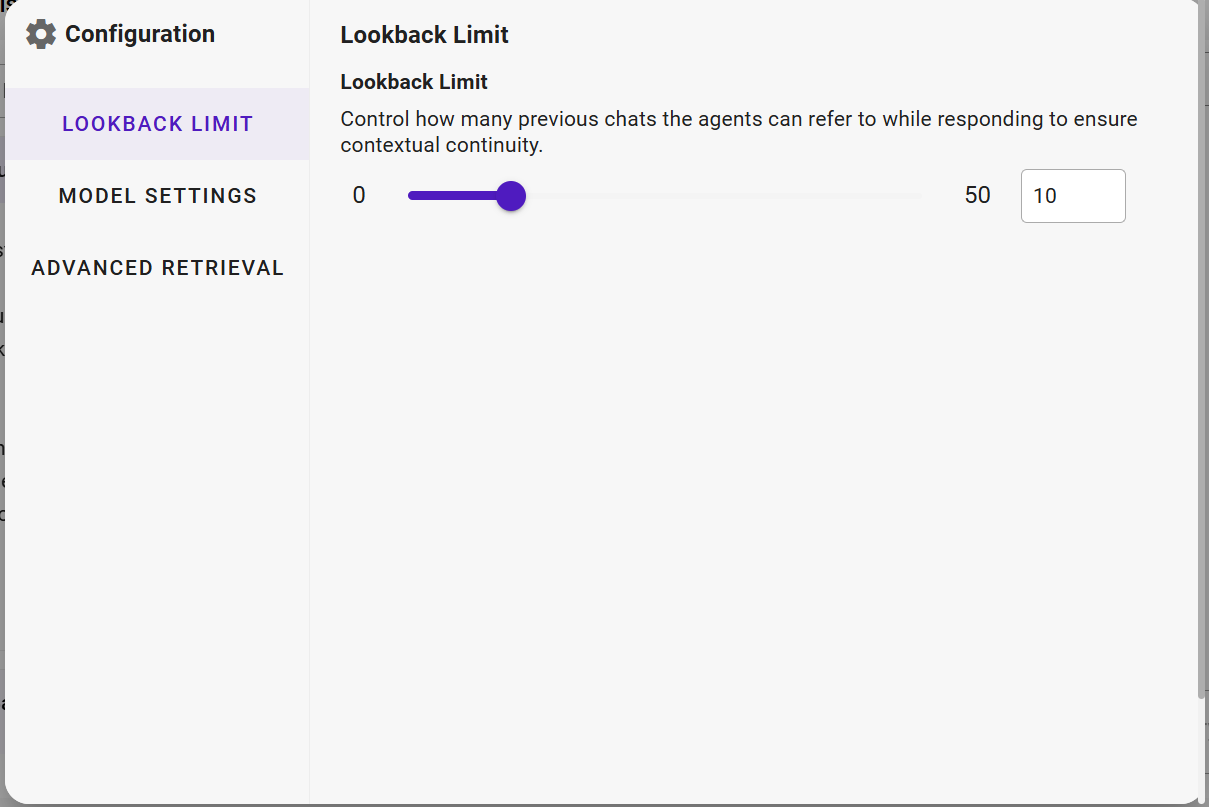
Defines how many previous conversations can be referenced from the history when generating a response to ensure the contextual continuity.
Default: 10
Range: 0–50
Example: If set to 5, the agent will only consider the last five interactions for context.
#
Model Settings
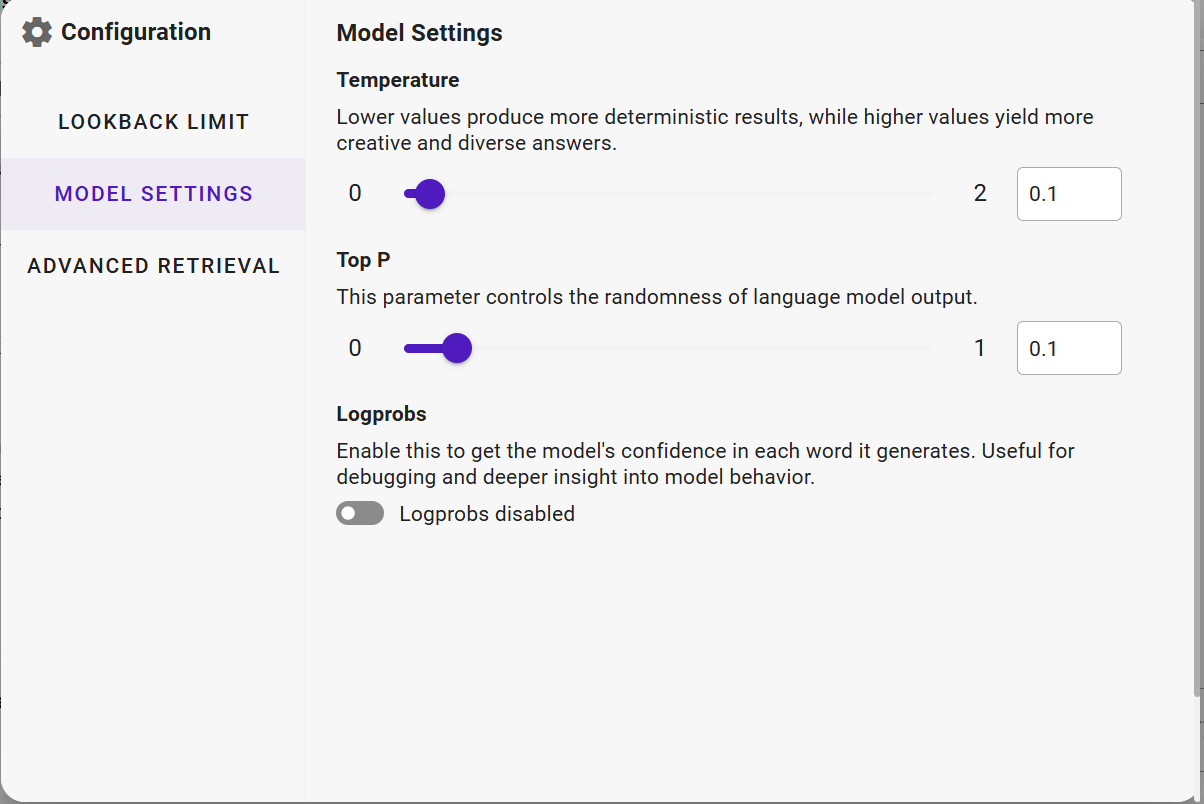
#
Temperature
Controls the creativity vs. predictability of the model’s responses.
Lower values → More focused, predictable, and consistent outputs.
Higher values → More creative, varied, and less deterministic responses.
Range: Typically 0–2 for GPT models; 0–1 for certain other models.
Example: 0.2 is ideal for compliance documentation; 1.0 is better for brainstorming ideas.
**Top‑P ** Controls how widely the AI considers different wording options when creating a response.
Lower values → The AI chooses from only the most likely words, giving more predictable and consistent answers.
Higher values → The AI considers a wider range of possible words, which can make responses more creative but less predictable.
Range: 0–1
Example: 0.9 allows diverse responses; 0.3 narrows to safer, more predictable answers.
#
Logprobs
Displays the model’s confidence score for each generated word, showing how certain the model is about its output.
- Availability: Only supported on Azure GPT‑4o models:
**Azure GPT‑4o‑mini **
**Azure GPT‑4o‑4K **
Azure GPT‑4o‑16K
This feature is not available for other LLMs in Purple Fabric.
Use Case: Debugging agent responses, fine‑tuning prompts, and analyzing model decision‑making.
Control: On/Off toggle.
Example: When enabled for a supported Azure GPT‑4o model, the system displays probabilities for each generated word, helping identify uncertainty or hesitation in the model’s responses.
#
Advanced Retrieval Settings
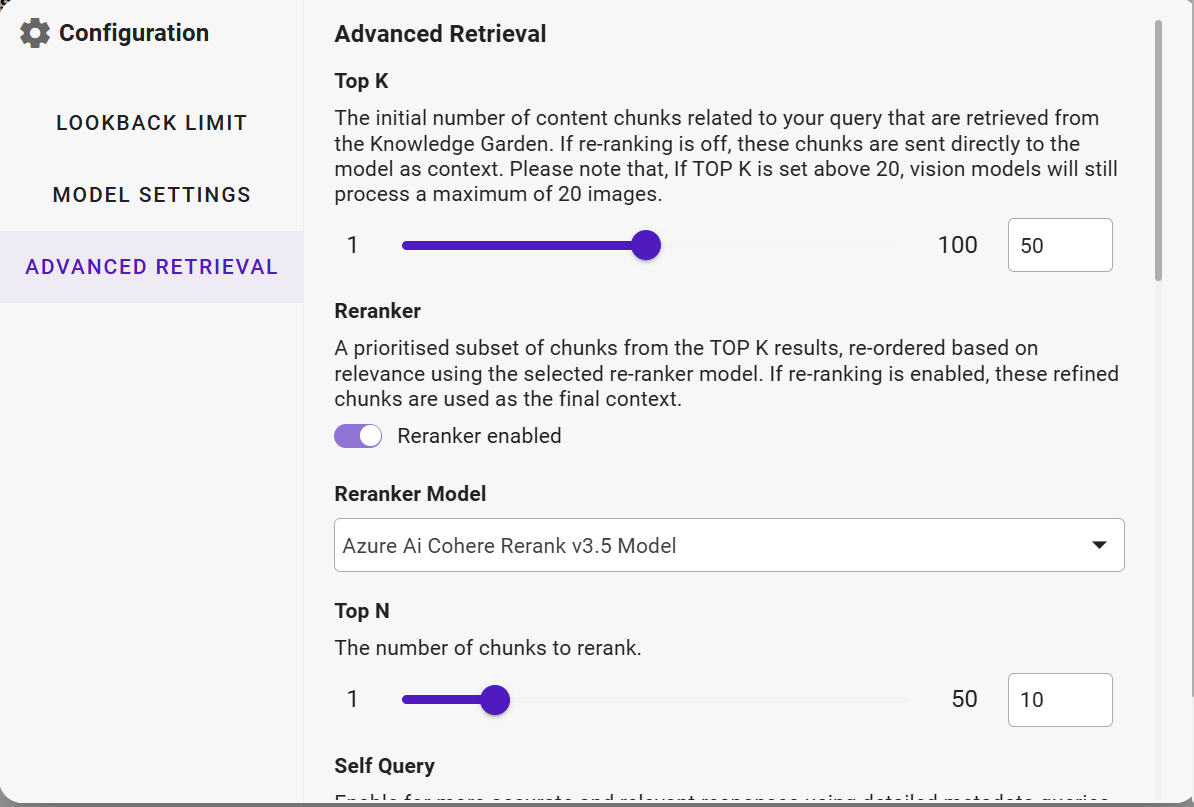
#
Top‑K
Specifies how many pieces of information (“chunks”) the system initially retrieves from the Enterprise Knowledge Garden (EKG) or other connected knowledge sources when answering a query.
If re‑ranking is off, all of these go straight to the model.
Vision models can still only work with up to 20 images, even if Top‑K is set higher.
Range: 1-100
Example: If you set Top‑K to 10, the system will pull the 10 most relevant chunks it can find.
#
Re‑ranker
Helps the system sort the Top‑K results so the best ones are used.
If enabled, only the most relevant chunks are kept for the final answer.
Toggle: On/Off
Example Model: *Azure AI Cohere Rerank v3.5 *
#
Top‑N
How many chunks from the Top‑K should be re‑ranked.
Range: 1–50
Example: If Top‑K is 10 and Top‑N is 5, the system will keep the 5 best chunks from the original 10.
#
Self‑Query (Toggle)
Enables the system to generate smarter, metadata‑driven queries to improve retrieval accuracy and surface more relevant results.
Pre‑requisite: The Enterprise Knowledge Garden (EKG) must contain chunks with properly tagged metadata (e.g., author, date, category) for Self‑Query to work effectively. Without metadata tags, the feature cannot optimize retrieval.
Benefit: Helps the agent filter and target information more precisely, improving the relevance of responses.
Example: If EKG chunks are tagged with “region” and “year”, the system can automatically refine a user query like “Show sales trends” into “Show sales trends in APAC for 2024” using metadata filters.
#
Research Mode (Toggle)
Slows things down slightly to dig deeper and be more precise — useful for complex questions or detailed analysis.
#
Research Mode Prompt
Special instructions you can set to guide the model when Research Mode is on, ensuring it focuses on exactly what you need.
#
Interaction Types
You define how your Digital Experts will engage with users or systems: conversational dialogue or automated execution.
- Conversation
Enables Digital Experts to engage in natural language dialogues with users, supporting multi‑turn interactions where context is maintained across multiple exchanges.
Function: Facilitate fluid, human‑like conversations that adapt to the user’s inputs over time.
Application: Customer support agents, virtual assistants.
- Automation
Enables Digital Experts to use input/output (I/O) schemas to define the structure of data they receive and produce, ensuring reliable integration with other systems and processes.
Function: Perform actions autonomously by processing structured inputs and delivering outputs in consistent, expected formats.
Application: Invoice Extractor, KYC Classifier, Claims Verification Expert.
#
Agent Add-ons 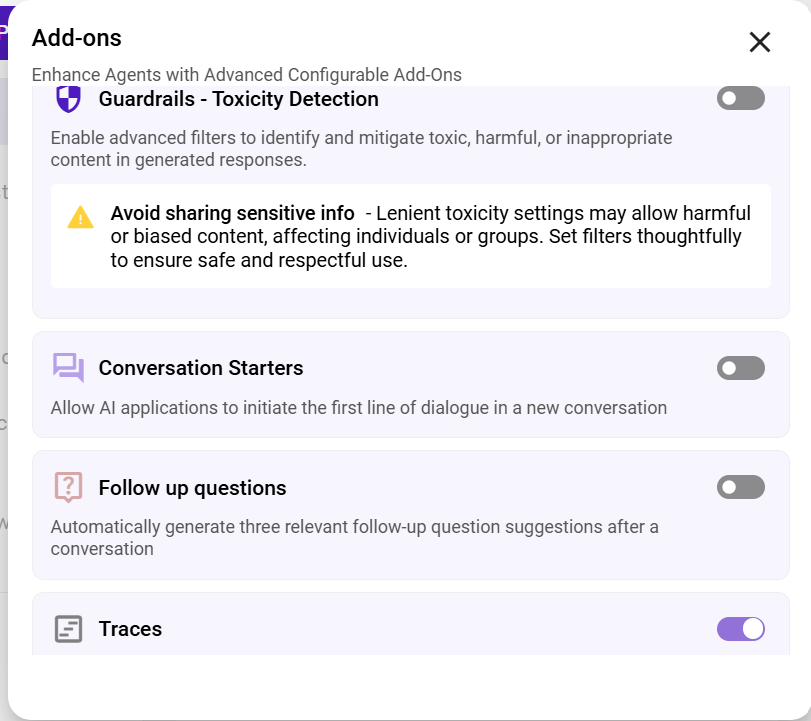
Add-ons are optional, configurable modules that extend your Digital Expert’s features beyond its primary functions.